Certified Scrum Developer

The Certified Scrum Developer™ (CSD) certification is the most respected development certification in the Agile Community. Technical team members often begin their transition towards application of agile engineering principles with this workshop.
As a prerequisite to the CSD you must first attend a two day, Scrum Alliance approved, session covering general agile and Scrum principles. This is typically achieved by attending a Certified Scrum Master (CSM) Workshop.
 The CSD Certification workshop is a three-day, hands-on, development workshop. Attendees learn how to create software they can be proud of by applying the Scrum framework and engineering practices made popular in Extreme Programming (XP).
The CSD Certification workshop is a three-day, hands-on, development workshop. Attendees learn how to create software they can be proud of by applying the Scrum framework and engineering practices made popular in Extreme Programming (XP).
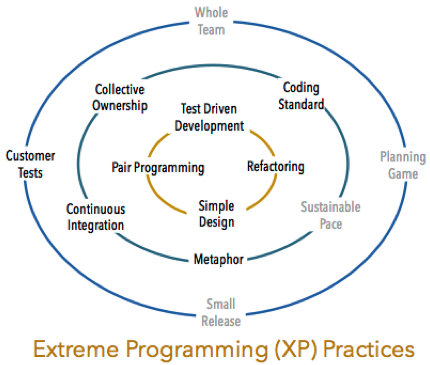
The diagram to the right shows the topics covered in the CSD Workshop. Topics shown in gray (Planning Game, Small Releases, Sustainable Pace, and Whole Team) are covered in the CSM Course.
The workshop is suitable for development team members including architects, coders, database developers, quality assurance, and others with technical knowledge. The class requires hands on programming in pairs, and different roles, such as quality assurance and developer, often work together during the workshop.
Participating actively in the session for all three days results in your certification as a Certified Scrum Developer (CSD). You and your team will gain a shared understanding that will facilitate the use of modern agile engineering principles.
Application of these principles will allow you to deliver software more frequently, with less defects, better internal quality (hitting all “ilities” such as testability, maintainability, reliability, scalability, etc.) while better aligning with business goals. Even more importantly, the code base and test automation get better over time thus making it easier and easier to add new functionality.
Who Should Attend
Programmers, Developers, Tech Leads

Agenda
Day One
- Agile Refresher
- Pairing
- Environmental Setup
- Automated Customer Tests
- Automated Unit Testing
- Continuous Integration
- Retrospective
Day Two
- Working with the PO
- Pair Programming
- Coding Standards
- Simple Design
- Test Driven Development (TDD)
- Retrospective
Day Three
- Refactoring
- Collective Ownership
- Continous Deployment
- Refactoring Legacy Code
- Question & Answers
- Session Wrap-Up
- Retrospective
Learning Objectives
| Area | Learning Objective |
|---|---|
| Test Driven Development (TDD) | Assist your staff with the paradigm shift to TDD by focusing on test automation then moving towards test first. |
| Pair Programming | Address worries about two doing the work of one, assist developers who won’t necessarily take well to pairing, create the physical setup and make pairing work with geographically distribution. |
| Refactoring | Help your teams balance current priorities against the desire to cleanup the code base to simplify future deliveries. |
| Simple Design | Provide guidance to your team on how to solve today’s problems with clean code that amenable to future change so that they don’t fall into the trap of complicating your system by solving future problems that may never occur. |
| Coding Standards | Help your team develop standards from the bottom up. |
| Collective Ownership | Coders often don’t want to give up ownership of the code they created. Help them act in a way that benefits the whole team and each individual. |
| Continuous Integration | Many teams already apply CI; learn how CI helps, and how to make it better. |
| Customer Tests | ATDD increases alignment between all stakeholders and increases quality but using ATDD requires business buy in, trained staff and new technology. Get ATDD going quickly by focusing on common understanding. |
| Customer Deployment | There is a technical leap from CI, to continuous delivery (SIT, UAT), to continuous deployment. We will briefly cover key topics like feature toggles. |
| Working with Legacy Code | Help your team untangle the systems you inherit. |